Using EPICS ADS
ADS Example IOC describes how to compile and run ADS sample IOC, which is provided as a reference implementation with the ADS device support library. ADS Device Support in a New IOC describes how to include ADS device support in a new IOC.
ADS Example IOC
ADS example IOC is provided as a reference IOC implementation with the ADS device support library. To successfully run the IOC, a connection with the PLC program running in TwinCAT XAE must be set up.
The example IOC is included as an EPICS application and is located in your $TOP/adsExampleApp/. This IOC contains the necessary records that connect to the variables of the example PLC program.
TwinCAT XAE
The PLC program can be found in the TC3_testProj directory in the ads-sample-ioc directory. This program can be used in conjunction with the ADS example IOC.
Configure ADS route
First, open the project in TwinCAT XAE, click SYSTEM -> Routes, then click the Add button. Fill in route parameters:
Route name: Descriptive name of the new route.
AmsNetId: AMS net ID of the IOC that will connect to the PLC program.
Address info: IP address of the IOC that will connect to the PLC program (i.e., IP of the host OS running the IOC).
Host name/IP address: Select IP address to match the above Address info specification.
Remote route: Set to None.
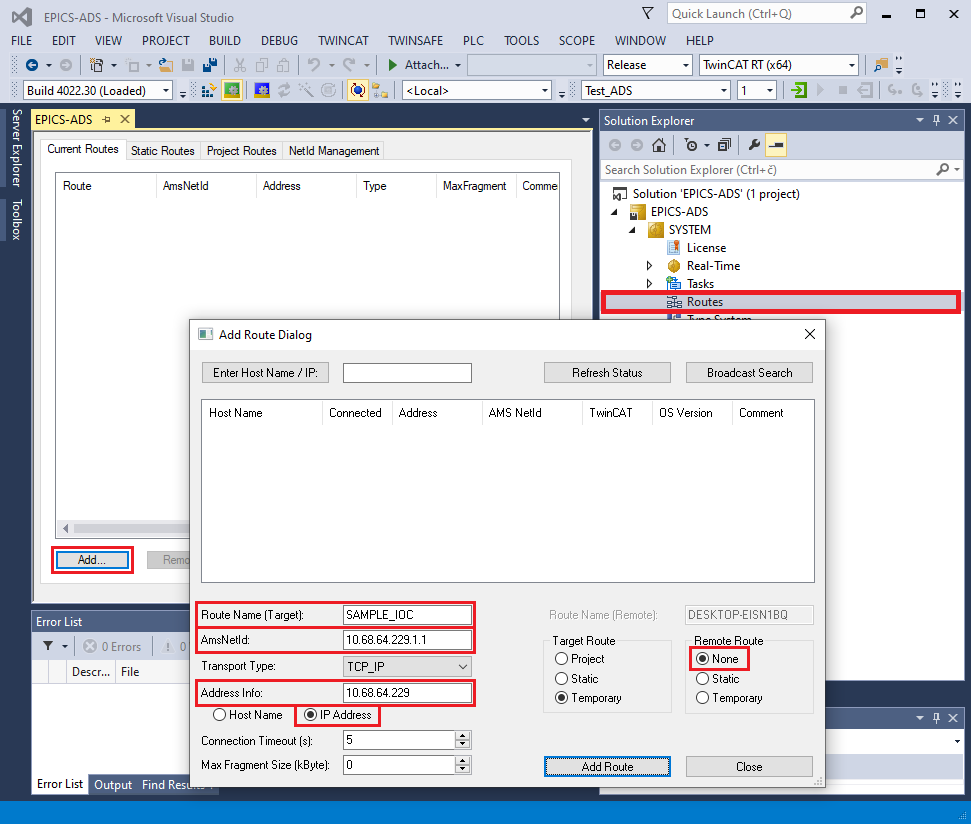
Example of add route dialog
Building PLC project
Next, right click on Test_ADS Project, then click Build to build the project.
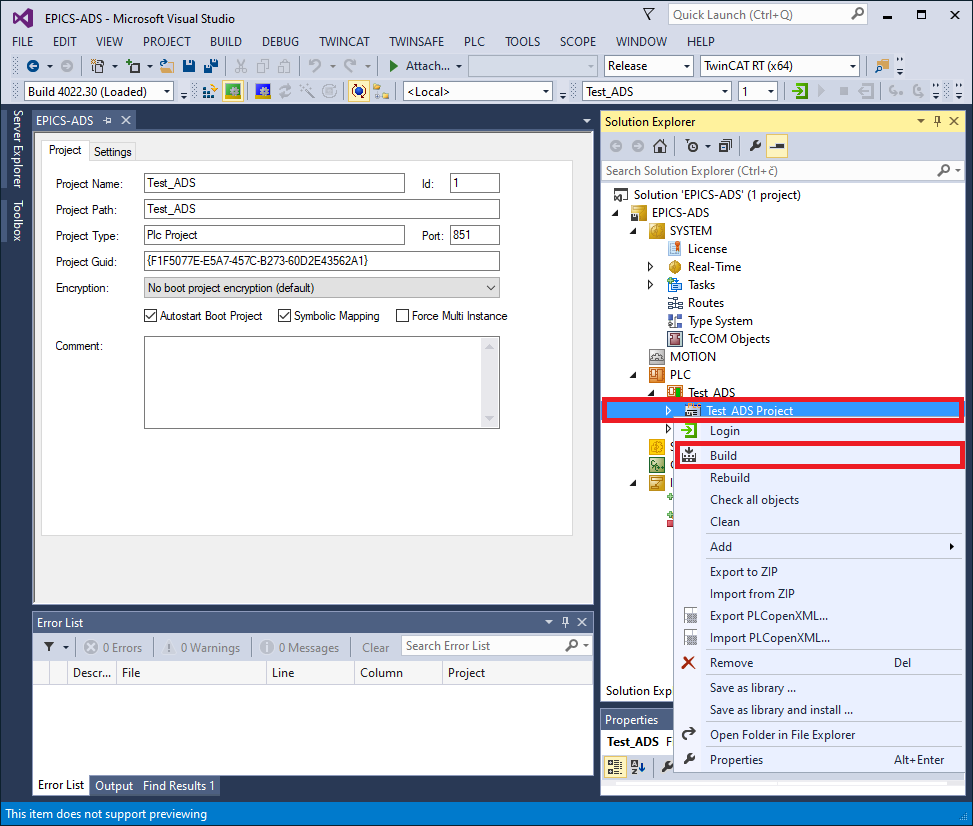
Building a TwinCAT project in XAE
Activating PLC project and Autostart
Assuming that the program compiled without errors, click on the Test-ADS and make sure that Autostart Boot Project is checked. Then right click on Test_ADS again and click Activate Boot Project.
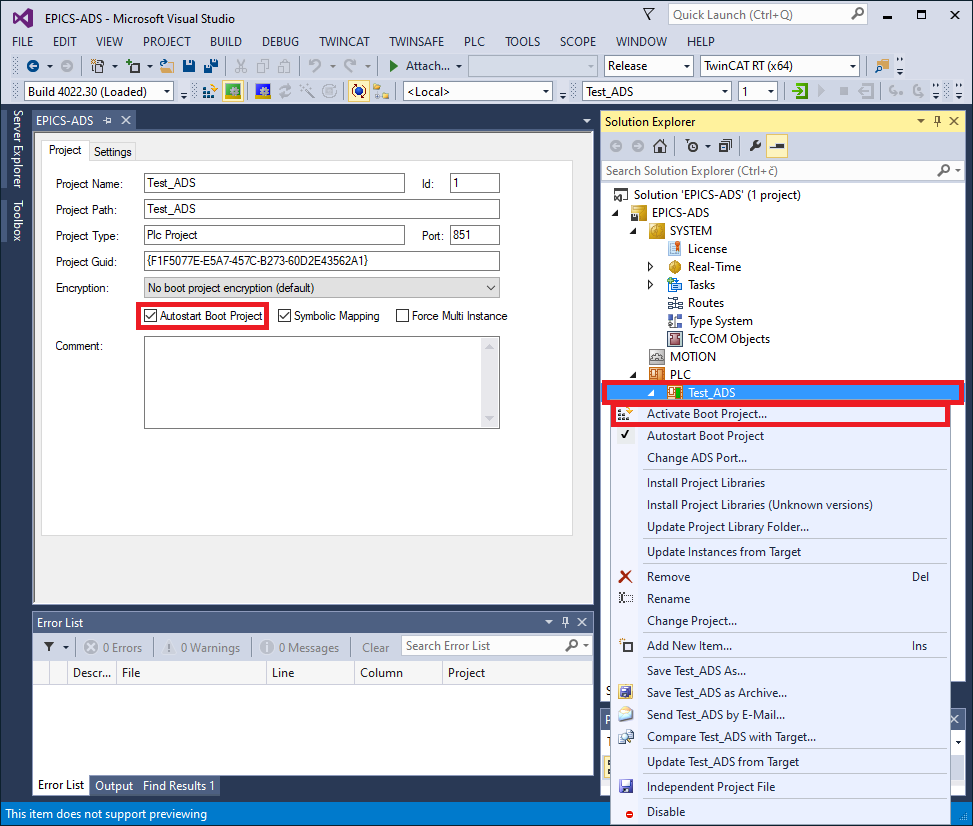
Activating a TwinCAT project in XAE
Activating Configuration
The last step is to activate the configuration by clicking TwinCAT -> Activate Configuration. Make sure that the PLC in in Run mode before connecting to the PLC with the IOC.
Using the Sample IOC
Configuring st.cmd
Two things need to be edited in st.cmd:
Change the local AMS net ID. This can be the same as the local IP address, with an additional “.1.1” suffix, e.g. 10.68.64.229.1.1). This local (IOC) AMS ID and IP address must be added as a route as described in TwinCAT section of this chapter.
Set the connection parameters for the host running the Test plan project PLC program:
IP_TEST_PLAN: IP address
AMS_ID_TEST_PLAN: AMS net ID
#!../../bin/linux-x86_64/adsExample
## Register all support components
dbLoadDatabase "../../dbd/adsExample.dbd"
ads_sample_registerRecordDeviceDriver pdbbase
# Set local AMS net ID
AdsSetLocalAMSNetID("10.68.64.229.1.1")
# Test Plan PLC program connection parameters
epicsEnvSet("PREFIX_ADSEXAMPLE", "ADS-EXAMPLE-01")
epicsEnvSet("PORT_ADSEXAMPLE", "ads-example-port")
epicsEnvSet("IP_ADSEXAMPLE", "10.68.6.45")
epicsEnvSet("AMS_ID_ADSEXAMPLE", "10.68.79.25.1.1")
# Load record instances for Test Plan PLC program
dbLoadRecords("../../db/example.db","P=$(PREFIX_ADSEXAMPLE), PORT=$(PORT_ADSEXAMPLE)")
# Open ADS port
AdsOpen("$(PORT_ADSEXAMPLE)", "$(IP_ADSEXAMPLE)", "$(AMS_ID_ADSEXAMPLE)")
# Enable asyn trace output for errors and warnings
asynSetTraceMask("$(PORT_TEST_PLAN)", 0, 0x21)
# Alternatively, output everything
#asynSetTraceMask("$(PORT_TEST_PLAN)", 0, 0xff)
iocInit
# End of IOC initialization
Running Sample IOC
Now that the simulated PLC is running in the TwinCAT XAE and the st.cmd is configured, the IOC can be started:
$ cd iocBoot/iocadsExample/
$ ../../bin/linux-x86_64/adsExample st.cmd
## Register all support components
dbLoadDatabase "dbd/adsExample.dbd"
adsExample_registerRecordDeviceDriver pdbbase
# Set local AMS net ID
AdsSetLocalAMSNetID("192.168.122.75.1.1")
# example PLC program connection parameters
epicsEnvSet("PREFIX_ADSEXAMPLE", "ADS-EXAMPLE-01")
epicsEnvSet("PORT_ADSEXAMPLE", "ads-example-port")
epicsEnvSet("IP_ADSEXAMPLE", "192.168.122.146")
epicsEnvSet("AMS_ID_ADSEXAMPLE", "10.0.2.15.1.1")
## Load record instances
dbLoadRecords("db/example.db","P=ADS-EXAMPLE-01, PORT=ads-example-port")
# Open ADS port
AdsOpen("ads-example-port", "192.168.122.146", "10.0.2.15.1.1")
[TRACE] ADSPortDriver.cpp:178 ADSPortDriver(): ADSPortDriver parameters: ads-example-port, 192.168.122.146, 10.0.2.15.1.1, 500, -1
[TRACE] ADSPortDriver.cpp:180 ADSPortDriver(): ADSPortDriver instance: 0x9464b0, ip: 192.168.122.146
# Enable asyn trace output for errors and warnings
asynSetTraceMask("ads-example-port", 0, 0x21)
# Alternatively, output everything
#asynSetTraceMask("$(PORT_ADSEXAMPLE)", 0, 0xff)
cd "/opt/epics/modules/ads-3.0.0/iocBoot/iocadsExample"
iocInit
Starting iocInit
############################################################################
## EPICS R7.0.4.1
## Rev. 2022-05-05T17:02+0200
############################################################################
[TRACE] ADSPortDriver.cpp:202 initHook(): ADSPortDriver instance: 0x9464b0, ip: 192.168.122.146
[TRACE] ADSPortDriver.cpp:232 connect(): ADSPortDriver instance: 0x9464b0, ip: 192.168.122.146
2022-06-13T14:52:42+0200 Info: Connected to 192.168.122.146
2022/06/13 14:52:42.050 [WARNING] ADSPortDriver.cpp:259 connect(): [ads-example-port] Connected to ADS device (IP: 192.168.122.146)
2022/06/13 14:52:42.050 [WARNING] ADSPortDriver.cpp:264 connect(): [ads-example-port] Resolving ADS variable names
iocRun: All initialization complete
## Start any sequence programs
#seq sncxxx,"user=vagrant"
epics> 2022/06/13 14:52:53.445 [WARNING] ADSPortDriver.cpp:291 connect(): [ads-example-port] Resolved 10016 read and 16 write variable names
2022/06/13 14:52:53.446 [WARNING] ADSPortDriver.cpp:305 connect(): [ads-example-port] Initialized sum-read request buffers
2022/06/13 14:52:53.496 [WARNING] ADSPortDriver.cpp:308 connect(): [ads-example-port] Inital sum-read status (0): OK
epics>
Refer to the Troubleshooting section if the IOC fails to connect to the ADS devices.
Note
Exiting the IOC using exit command (or ctrl-d) may output errors describing the port being disabled. This is normal behavior. EPICS scan threads continue to work even after exit hooks are called, which can result in device support locking the non-existent driver. To prevent issues from that, port driver is disabled at IOC exit.
Note
The ads-sample-ioc repository contains GUI screens for the simulated PLC (adsExampleApp/exampleScreens/adsExample.bob) which can be open in Phoebus.
ADS Device Support in a New IOC
This example shows how to create a new IOC with the ADS device support included. For this example, create a new IOC using makeBaseApp.pl:
$ mkdir test-ioc
$ cd test-ioc/
$ makeBaseApp.pl -t ioc test
$ makeBaseApp.pl -i -t ioc test
Using target architecture linux-x86_64 (only one available)
The following applications are available:
test
What application should the IOC(s) boot?
The default uses the IOC's name, even if not listed above.
Application name? test
Which should produce a directory structure similar to this:
$ ls -R
.:
configure iocBoot Makefile testApp
./configure:
CONFIG CONFIG_SITE Makefile RELEASE RULES RULES_DIRS RULES.ioc RULES_TOP
./iocBoot:
ioctest Makefile
./iocBoot/ioctest:
Makefile st.cmd
./testApp:
Db Makefile src
./testApp/Db:
Makefile
./testApp/src:
Makefile testMain.cpp
Now add the required ADS EPICS modules to the configure/RELEASE file: ASYN and ADS. It is not necessary to set the AUTOPARAM module path, since it is linked with the ADS port driver library. Also, because the IOC was created using makeBaseApp.pl, the EPICS_BASE should already be pointing to the correct location:
# RELEASE - Location of external support modules
...
# Variables and paths to dependent modules:
#MODULES = /path/to/modules
#MYMODULE = $(MODULES)/my-module
ASYN = /opt/epics/modules/asyn
ADS = /opt/epics/modules/ads
# If using the sequencer, point SNCSEQ at its top directory:
#SNCSEQ = $(MODULES)/seq-ver
# EPICS_BASE should appear last so earlier modules can override stuff:
EPICS_BASE = /opt/epics/base
# Set RULES here if you want to use build rules from somewhere
# other than EPICS_BASE:
...
Edit the IOC’s src/Makefile and include asynDriver and ADS driver’s DBD and library files. It is not necessary to include DBD and library files from the autoparamDriver module.
TOP=../..
include $(TOP)/configure/CONFIG
#----------------------------------------
# ADD MACRO DEFINITIONS AFTER THIS LINE
#=============================
#=============================
# Build the IOC application
PROD_IOC = test
# test.dbd will be created and installed
DBD += test.dbd
# test.dbd will be made up from these files:
test_DBD += base.dbd
# Include dbd files from all support applications:
#test_DBD += xxx.dbd
test_DBD += asyn.dbd ads.dbd
# Add all the support libraries needed by this IOC
#test_LIBS += xxx
test_LIBS += asyn ads
# test_registerRecordDeviceDriver.cpp derives from test.dbd
test_SRCS += test_registerRecordDeviceDriver.cpp
# Build the main IOC entry point on workstation OSs.
test_SRCS_DEFAULT += testMain.cpp
test_SRCS_vxWorks += -nil-
# Add support from base/src/vxWorks if needed
#test_OBJS_vxWorks += $(EPICS_BASE_BIN)/vxComLibrary
# Finally link to the EPICS Base libraries
test_LIBS += $(EPICS_BASE_IOC_LIBS)
#===========================
include $(TOP)/configure/RULES
#----------------------------------------
# ADD RULES AFTER THIS LINE
Compile the IOC:
$ make
make -C ./configure install
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/epics-dev/test-ioc/configure'
perl -CSD /opt/epics/base/bin/linux-x86_64/makeMakefile.pl O.linux-x86_64 ../..
mkdir O.Common
make -C O.linux-x86_64 -f ../Makefile TOP=../.. \
T_A=linux-x86_64 install
... <output removed for brevity>
make -C ./iocBoot install
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/epics-dev/test-ioc/iocBoot'
make -C ./ioctest install
make[2]: Entering directory `/home/epics-dev/test-ioc/iocBoot/ioctest'
perl -CSD /opt/epics/base/bin/linux-x86_64/convertRelease.pl -t /home/epics-dev/test-ioc envPaths
make[2]: Leaving directory `/home/epics-dev/test-ioc/iocBoot/ioctest'
make[1]: Leaving directory `/home/epics-dev/test-ioc/iocBoot'
Assuming the compilation step was successful, you can run the IOC and check if ADS port driver commands are available in the IOC shell:
$ cd iocBoot/ioctest/
$ ../../bin/linux-x86_64-debug/test st.cmd
#!../../bin/linux-x86_64/test
## You may have to change test to something else
## everywhere it appears in this file
< envPaths
epicsEnvSet("IOC","ioctest")
epicsEnvSet("TOP","/home/epics-dev/test-ioc")
epicsEnvSet("ASYN","/opt/epics/modules/asyn")
epicsEnvSet("ADS","/opt/epics/modules/ads")
epicsEnvSet("EPICS_BASE","/opt/epics/base")
cd "/home/epics-dev/test-ioc"
## Register all support components
dbLoadDatabase "dbd/test.dbd"
test_registerRecordDeviceDriver pdbbase
## Load record instances
#dbLoadRecords("db/xxx.db","user=andrej")
cd "/home/epics-dev/test-ioc/iocBoot/ioctest"
iocInit
Starting iocInit
############################################################################
## EPICS R3.15.5
## EPICS Base built Aug 31 2018
############################################################################
iocRun: All initialization complete
## Start any sequence programs
#seq sncxxx,"user=andrej"
Run help command and verify that the ADS port driver commands are available, i.e. AdsOpen and AdsSetLocalAMDSNetID:
epics> help
Type 'help <command>' to see the arguments of <command>.
AdsFindIOIntrRecord AdsOpen
AdsSetLocalAMSNetID ClockTime_Report
ClockTime_Shutdown asDumpHash asInit asSetFilename
asSetSubstitutions ascar asdbdump asphag
aspmem asprules aspuag astac
asynAutoConnect asynEnable asynInterposeEosConfig
asynInterposeFlushConfig asynOctetConnect
asynOctetDisconnect asynOctetFlush asynOctetGetInputEos
... <output removed for brevity>
You now have a functional IOC that can use the ADS protocol to communicate with ADS capable devices. What is missing is a functional database with record configuration for the ADS device that you are connecting to the IOC, and an open ADS connection between them.
Refer to the ADS example IOC sources to see an example how the EPICS database is configured and how to open an ADS client connection from the IOC to an ADS device. Refer to Reference Manual for record configuration and IOC command description.